

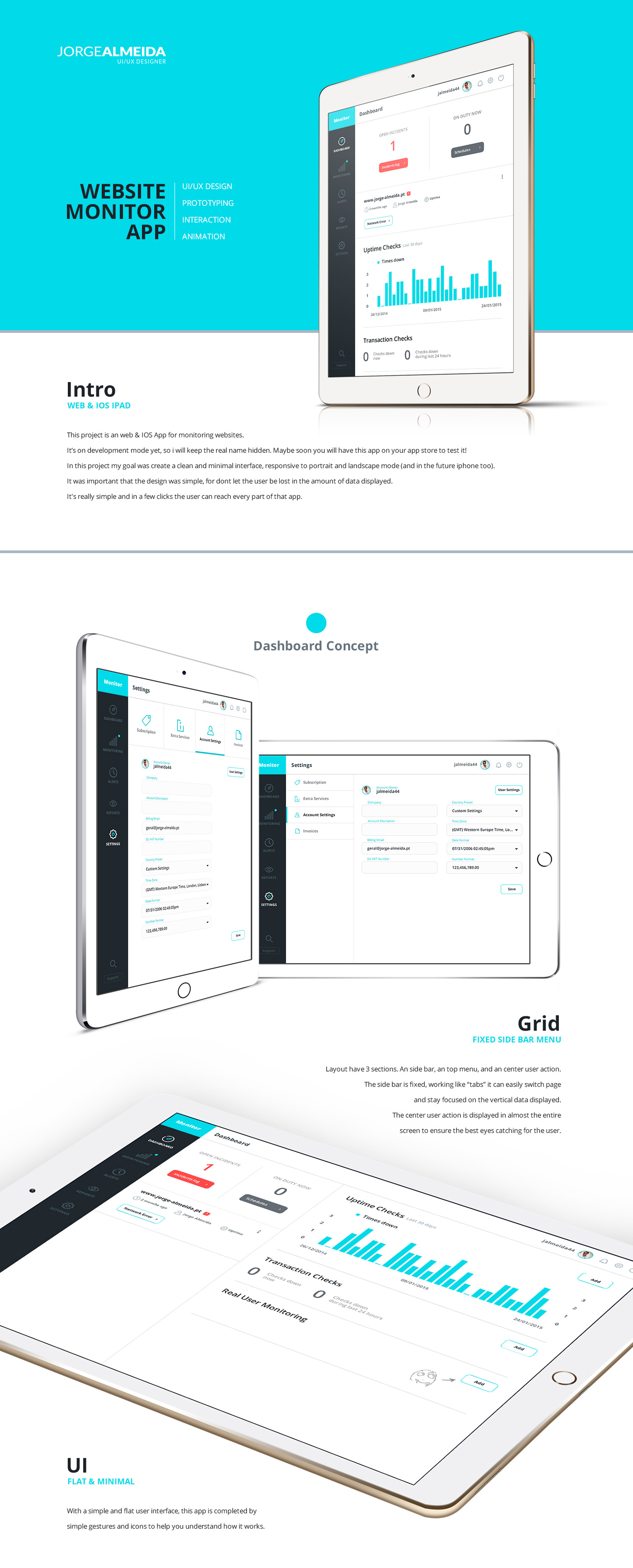
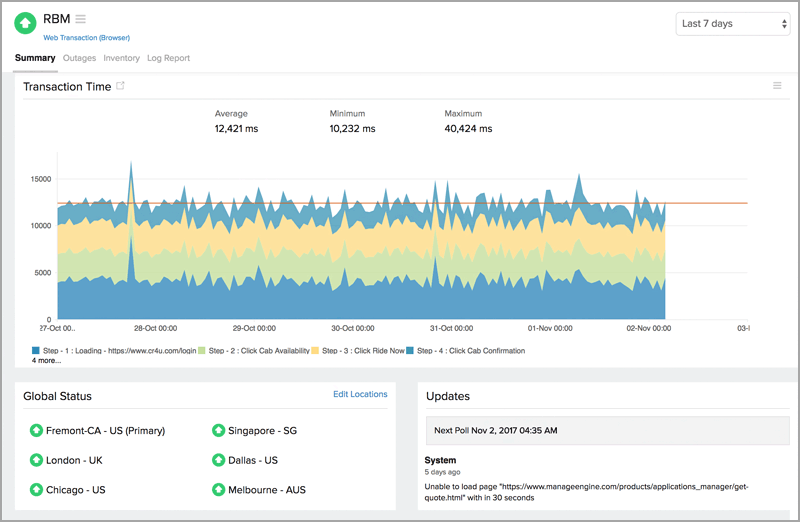
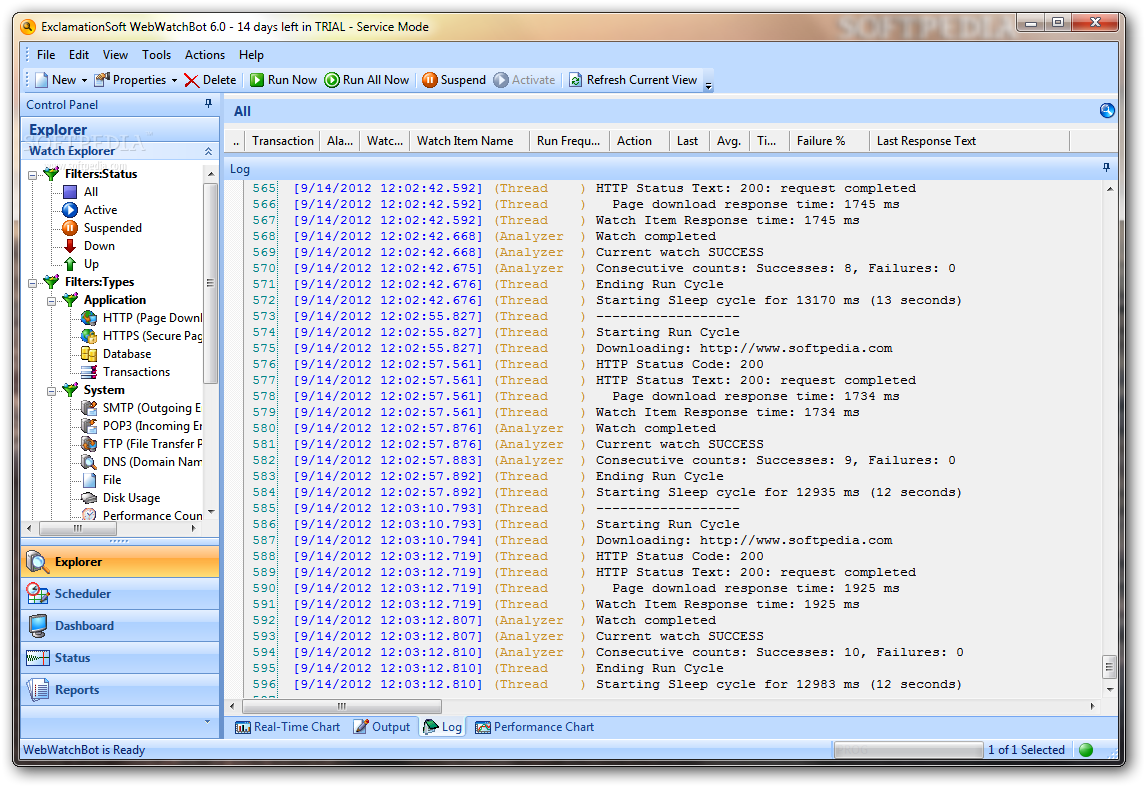
Typically, a monitor type will fall into one of the previously mentioned categories, although the more advanced monitors may cover all three. Website Monitoring involves testing websites for availability, performance, and function and alerting support staff when the page doesn’t work as expected. What types of Website Monitoring are there? RUM provides real user insights, but RUM relies on user interaction with the website to get data making it an unviable method for tracking uptime.
WEBSITE MONITOR CODE
Known as Real User Monitoring (RUM), script files, agents, cookies, or server-side code track the website’s performance as each site visitor accesses the site. Monitoring may also use data coming from the actual users of the website or service. If the result includes errors or slow response times, the service may initiate the check again from a different checkpoint to verify a persistent error before alerting the website’s support team. Reports its findings back to the monitoring service.Attempts to log in, conduct a search, use a shopping cart, even complete a purchase (web-application monitoring).Records load times for each page element as it loads in the browser (performance monitoring).Loads the content into a real browser (Real Browser Monitoring).Checks the return for specified content.For basic availability, the checkpoint reports the result and considers the test complete, but for more advanced monitoring the checkpoint continues. Checks the return for a response code.Initiates a connection with the website or service.The monitoring system designates a checkpoint to test the site, and the checkpoint may go through several steps to conduct the test. This network of computer checkpoints interacts with a website or service to verify that the service works as expected. How does Website Monitoring work?Īutomated Website Monitoring uses a network of computers located near the site’s end users. This article discusses primarily Synthetic Monitoring.
WEBSITE MONITOR MANUAL
Manual testing is sporadic and undependable when considering the number of variables that influence a site’s availability, performance, and function. Typically, the term refers to automated testing or Real User Monitoring (RUM), but some sites still do not test at all or rely on periodic checks performed by employees. The term “Website Monitoring” refers to any activity that checks the availability, performance, and function of a website or web service.
A Website Monitoring service checks and verifies that the site is up and working and site visitors can use the site as expected. It also provides users insight into the European Commission’s comparative analysis.Website Monitoring is an all-encompassing term for any activity that involves testing a website or web service for availability, performance, or function. The Monitor Toolbox strengthens the cross-EU knowledge of education and training systems and their broad variation across Member States. It puts a spotlight on the context that the EU-level target and indicator domains are embedded in.
The Monitor Toolbox provides an overview of the key indicators used in the Education and Training Monitor. The country reports are based on the most up-to-date quantitative and qualitative evidence available. They provide the reader with more in-depth insights into the performance of countries with regard to the EU-level targets agreed as part of the EEA strategic framework. The Education and Training Monitor’s country reports capture recent and ongoing policy development at all education levels in the 27 EU Member States. In addition, the 2022 edition starts with a brand-new EU-level indicator that can be used as a broad measure of the equity of EU education and training systems. 7 EU-level targets have been set, and this report complements them with numerous supporting indicators to shed light on context and possible policy levers. The Education and Training Monitor’s comparative report tracks progress towards achieving the EU-level targets agreed as part of the EEA strategic framework. The Education and Training Monitor consists of the following parts: Comparative report: progress towards EU-level targets
These contribute towards the monitoring of the European Education Area (EEA) strategic framework, with the 2022 edition of the Monitor as part of the EEA Progress Report. The Monitor brings together the latest available data and other evidence, alongside updates on national policy measures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
